Android笔记
xml中的各种字符串数据建议放在values目录下的string.xml中
<resources> <string name="app_name">HelloWorld</string> </resources>
1. 活动
1.1 创建活动
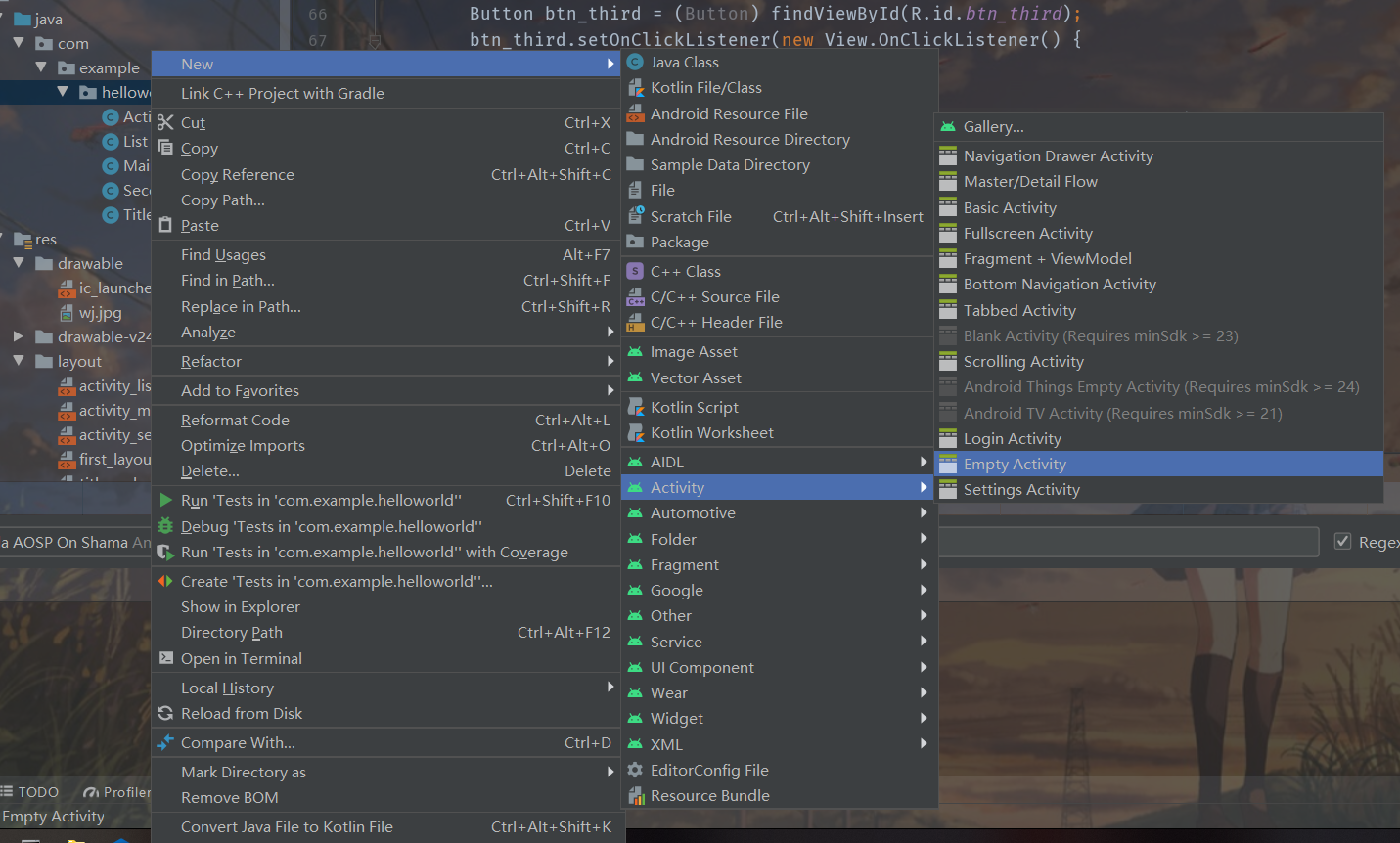
在包下右键创建新的活动
1.2 创建并加载布局
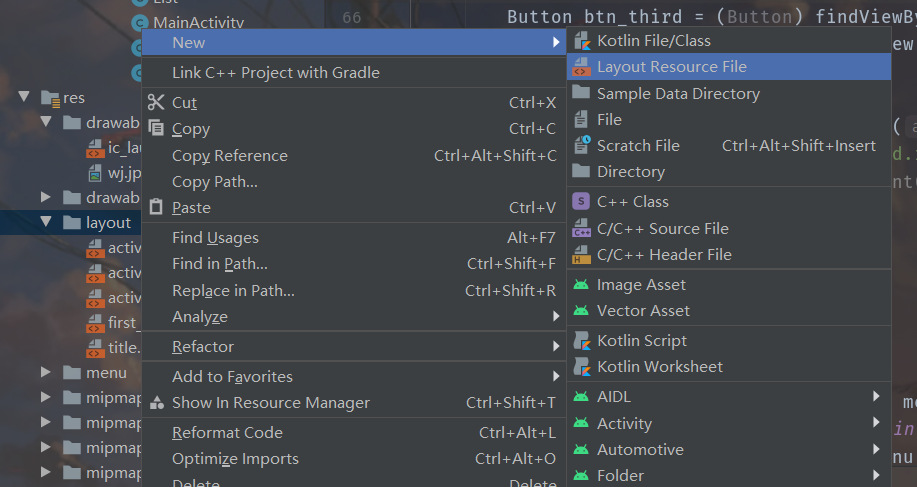
在资源目录下的layout文件夹下右键创建新的布局资源(Android Studio默认创建)
配置好布局之后在活动类下添加布局
public class List extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_list);
}
1.3在活动中使用Toast
Toast是安卓应用中一种比较常用的提示方式
添加方法也比较简单
Toast.makeText(this, "click add", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
makeText方法参数:
- this:上下文,如果嵌套太深this指向会错误,可改为当前活动.this、getContext(),也可以在外层定义一个
Context that = this;用来传递this - “click add”:字符串,Toast要显示的信息,可以是变量
- Toast.LENGTH.SHORT:显示时间2秒,LONG是3.5秒
show()方法不要忘记添加
1.4在活动中使用menu
在res下创建menu目录,新建xml文件,内容格式如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<menu xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<item android:id="@+id/add_item"
android:title="Add"/>
<item android:id="@+id/sub_item"
android:title="Sub"/>
</menu>
在要添加menu的活动中添加菜单,格式如下
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return super.onCreateOptionsMenu(menu);
}
@Override
public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(@NonNull MenuItem item) {
Context that = this;
switch (item.getItemId()) {
case R.id.add_item:
Toast.makeText(that, "click add", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.sub_item:
Toast.makeText(this, "click sub", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
default:
break;
}
return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item);
}
1.5在活动之间穿梭
一个安卓应用通常不止一个活动,需要在不同的活动之间来回穿梭来完成各种操作
1.5.1显式穿梭
顾名思义,显示穿梭很明显能看出要跳转到那个活动
在页面中有一个按钮,点击按钮触发切换活动的事件
Button btn_third = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_third);
btn_third.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent3 = new Intent(MainActivity.this, List.class);
startActivity(intent3);
}
});
先给button添加事件监听,当触发时间时,使用Intent穿梭事件
Intent构造函数:
- MainActivity.this:上下文
- List.class:要跳转的活动(反射)
活动需要在Mainfest中注册,这些在创建活动时Android Studio默认添加了,如果没有会报错
1.5.2隐式穿梭
隐式穿梭不会很容易看出要跳转的目的、
首先,隐式穿梭需要配置Mainfest
<activity android:name=".List">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="com.example.hello.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<category android:name="com.example.hello.MY_CATEGORY" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
然后在跳转时使用另一种方式
Button btn_third = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn_third);
btn_third.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent3 = new Intent("com.example.hello.MAIN");
// 只使用了android.intent.category.DEFAULT,这里可以不添加category,如果自定义了category就必须要添加
intent3.addCategory("com.example.hello.MY_CATEGORY");
startActivity(intent3);
}
});
配置时注意action和category的包路径,只有action和category一致才会进行跳转
更多隐式穿梭用法
跳转网页
点击事件如下
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse("http://www.baidu.com"));
startActivity(intent);
在Mainfest对应事件中添加data标签
<activity android:name=".SecondActivity">
<intent-filter tools:ignore="AppLinkUrlError">
<action android:name="android.intent.action.VIEW" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.DEFAULT" />
<data android:scheme="http" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
拨打电话

1.5.3 活动之间传递数据
在许多情况下,活动之间切换需要携带数据,Intent提供了putExtra方法来传递数据,在MainActivity中通过按钮触发事件,携带参数跳转到SecondActivity
Button btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, SecondActivity.class);
intent.putExtra("extra_value1", 10);
intent.putExtra("extra_value2", "by first");
startActivityForResult(intent, 1);
}
});
startActivityForResult(intent, 1);不同的请求通过请求码进行区分
在SecondActivity中接收参数并显示到页面上
final Intent intent = getIntent();
String str = intent.getStringExtra("extra_value2");
int i = intent.getIntExtra("extra_value1", -1);
// int类型的数据接收时可以设置默认值
String string = str + i;
TextView textView = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.textView);
textView.setText(string);
1.5.4向上一个活动返回数据
当然,SecondActivity也可以向MainActivity传递数据
@Override
public void onBackPressed() {
// super.onBackPressed();
Intent intent1 = new Intent();
intent1.putExtra("data_return", "I am second");
setResult(RESULT_OK, intent1);
finish();
}
当按下返回键时(可以通过其他事件触发),向主页面传递数据,这里要设置result返回的状态
在主活动中接收SecondActivity传回来的数据
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, @Nullable Intent data) {
super.onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data);
switch (requestCode) {
case 1:
if (resultCode == RESULT_OK) {
assert data != null;
String returnStr = data.getStringExtra("data_return");
Toast.makeText(this, returnStr, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
onActivityResult(requestCode, resultCode, data)
- requestCode:请求码,在发送请求时携带的code
- resultCode:响应码,活动返回数据时设置的code
- data:接收的数据
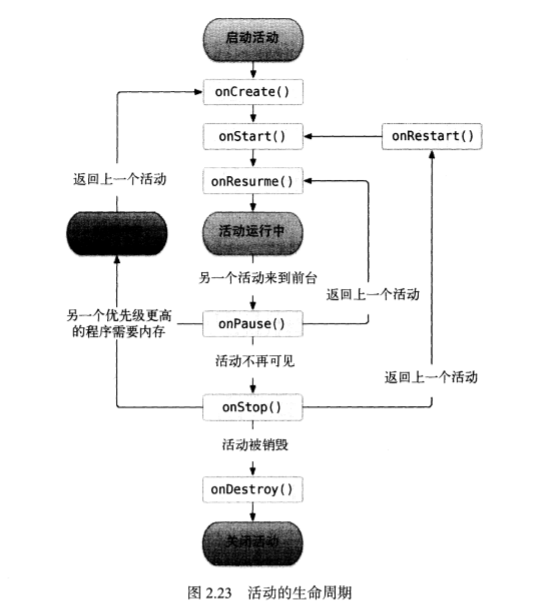
1.6 活动的生命周期
1.7 活动的启动模式
参考活动的启动模式
2. UI
组件相关省略
2.1 布局
2.1.1 线性布局LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"控制宽度,父组件的宽度,改为wrap_content就是自身元素的宽度android:layout_height="match_parent"控制高度android:orientation="vertical"控制纵向排列,如果改为vertical就会变为水平排列android:layout_gravity="right"控制元素的对齐方式android:layout_weight="1"类似于css中的flex:1
2.1.2 相对布局RelativeLayout
相对于parent进行定位
android:layout_alignParentLeft=”true”
android:layout_alignParentright=”true”
android:layout_alignParentTop=”true”
android:layout_alignParentBottom=”true”
android:layout_centerInParent=”true”
相对于控件进行定位
android:layout_above=”@id/button3”上
android:layout_below=”@id/button3”下
android:layout_toLeftOf=”@id/button3”
android:layout_toRightOf=”@id/button3”
android:layout_alignBottom=”@id/button3”两个控件底边对齐
alignBottom、alignTop、alignLeft、alignRight
2.1.3帧布局FrameLayout
2.1.4 百分比布局
由Android X支持库提供
导入支持库
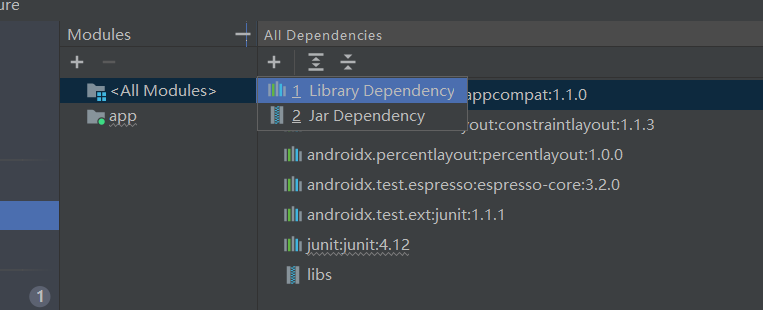
搜索percentLayout,添加依赖
然后布局文件中使用百分比布局
<androidx.percentlayout.widget.PercentFrameLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/imageView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="right"
app:layout_widthPercent="50%"
android:src="@drawable/wj"
tools:ignore="RtlHardcoded" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_close"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="left"
app:layout_widthPercent="50%"
android:text="关闭" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.percentlayout.widget.PercentFrameLayout>
2.2 控件
2.2.1 创建自定义控件
首先新建控件的title.xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:id="@+id/back_btn_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#409eff"
android:text="返回" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="#409eff"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:text="TextView" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/edit_btn_title"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#409eff"
android:text="菜单" />
</LinearLayout>
然后在想要引入title的布局中引入<include layout="@layout/title" />即可
但是这样给title控件添加事件的时候需要给每一个活动都添加,太过于繁琐
于是有了简便的方法
public class TitleLayout extends LinearLayout {
public TitleLayout(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.title, this);
Button back_btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.back_btn_title);
Button edit_btn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.edit_btn_title);
back_btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
((Activity)getContext()).finish();
}
});
edit_btn.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Toast.makeText(getContext(), "click edit", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
然后在想要引入控件的活动xml中使用包名引入
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<com.example.helloworld.TitleLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1" />
</LinearLayout>
2.2.2 ListView列表控件
首先创建ListView布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
然后在活动中添加
public class List extends AppCompatActivity {
private String[] data = {"apple", "banana", "peach", "fire",
"apple", "banana", "peach", "fire",
"apple", "banana", "peach", "fire",
"apple", "banana", "peach", "fire"};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_list);
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(List.this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, data);
ListView listView = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
listView.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
定制ListView
图标
新建一个菜单类,属性是名称和图标
public class Fruit {
private String name;
private int imageId;
public Fruit(String name, int imageId) {
this.name = name;
this.imageId = imageId;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getImageId() {
return imageId;
}
}
新建list选项布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<ImageView
android:id="@+id/fruit_image"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/fruit_name"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
新建适配器继承自ArrayAdapter
public class FruitAdapter extends ArrayAdapter {
private int resourceId;
public FruitAdapter(@NonNull Context context, int resource, @NonNull List<Fruit> objects) {
super(context, resource, objects);
resourceId = resource;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public View getView(int position, @Nullable View convertView, @NonNull ViewGroup parent) {
Fruit fruit = (Fruit) getItem(position);
@SuppressLint("ViewHolder") View view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resourceId, parent, false);
ImageView fruitImage = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_image);
TextView fruitName = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_name);
fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.getImageId());
fruitName.setText(fruit.getName());
return view;
}
}
最后再修改List活动
public class FruitList extends AppCompatActivity {
private List<Fruit> fruitList = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_list);
addData();
FruitAdapter fruitAdapter = new FruitAdapter(FruitList.this, R.layout.fruit_item, fruitList);
ListView listView = (ListView)findViewById(R.id.list);
listView.setAdapter(fruitAdapter);
}
// 初始化list
private void addData() {
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
Fruit apple = new Fruit("apple", R.drawable.icon);
fruitList.add(apple);
}
}
}
然后运行出来的List就带上了图标
点击事件
在List活动中添加事件监听
listView.setOnItemClickListener(new AdapterView.OnItemClickListener() {
@Override
public void onItemClick(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
Fruit fruit = fruitList.get(position);
Toast.makeText(FruitList.this, fruit.getName(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
优化
public View getView(int position, @Nullable View convertView, @NonNull ViewGroup parent) {
Fruit fruit = (Fruit) getItem(position);
// @SuppressLint("ViewHolder") View view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resourceId, parent, false);
View view;
if(convertView == null) {
view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resourceId, parent, false);
} else {
view = convertView;
}
ImageView fruitImage = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_image);
TextView fruitName = (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_name);
fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.getImageId());
fruitName.setText(fruit.getName());
return view;
}
对convertView进行判断,当为空时使用LayoutInflater加载布局,不为空时直接使用convertView,提高了运行效率
public class FruitAdapter extends ArrayAdapter {
private int resourceId;
public FruitAdapter(@NonNull Context context, int resource, @NonNull List<Fruit> objects) {
super(context, resource, objects);
resourceId = resource;
}
@NonNull
@Override
public View getView(int position, @Nullable View convertView, @NonNull ViewGroup parent) {
Fruit fruit = (Fruit) getItem(position);
// @SuppressLint("ViewHolder") View view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resourceId, parent, false);
View view;
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if(convertView == null) {
view = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(resourceId, parent, false);
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.fruitImage = (ImageView)view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_image);
viewHolder.fruitName = (TextView)view.findViewById(R.id.fruit_name);
view.setTag(viewHolder);
} else {
view = convertView;
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) view.getTag();
}
viewHolder.fruitImage.setImageResource(fruit.getImageId());
viewHolder.fruitName.setText(fruit.getName());
return view;
}
class ViewHolder {
ImageView fruitImage;
TextView fruitName;
}
}
修改FruitAdapter,新建内部类,对控件实例进行缓存,新建实例时通过setTag方法将实例存储,convertView不为空时使用getTag获取缓存的实例
2.2.3 RecycleView
3. 碎片
碎片可以有效解决手机平板分辨率不同产生的布局难看的问题,当屏幕分辨率大的时候引入两个碎片
3.1 碎片使用
创建碎片
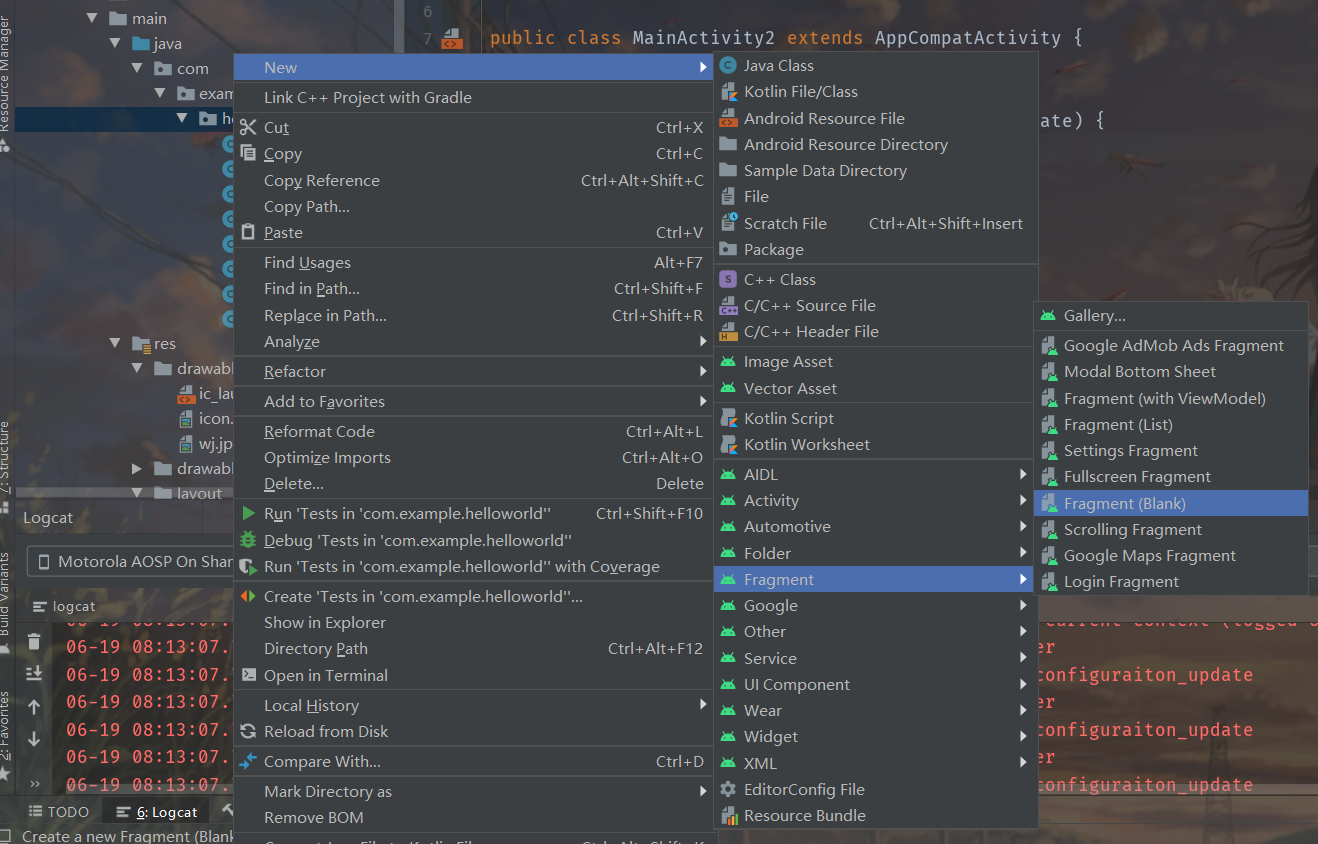
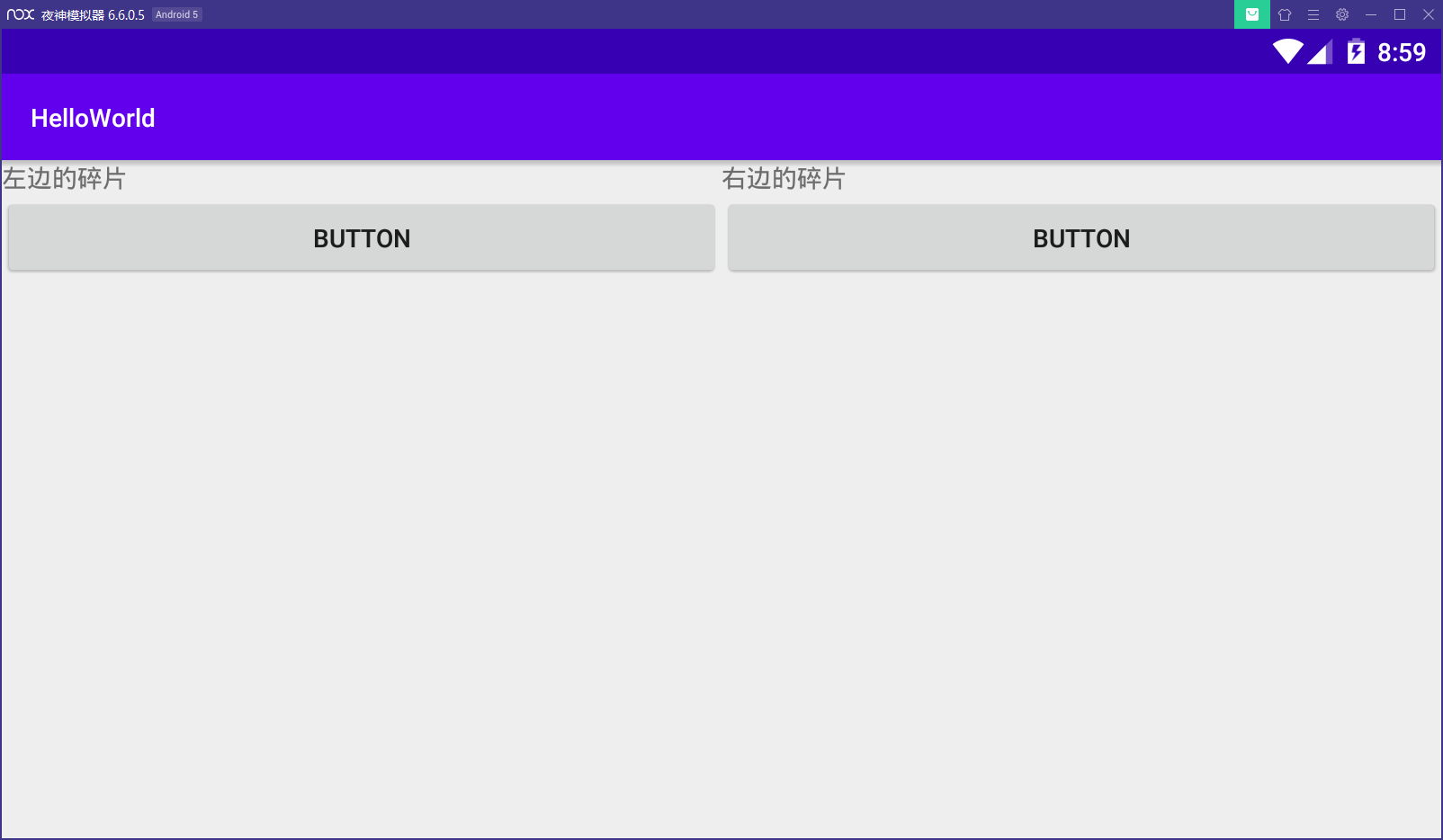
设置好碎片布局之后在活动的xml布局中引入fragment,选择要引入的碎片,调整布局
效果如图
3.2 动态使用碎片
再创建一个新的右侧碎片
修改当前活动
public class MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
Button button = (Button)findViewById(R.id.left_btn);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
replaceFragment(new FragmentRight());
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.left_btn:
replaceFragment(new FragmentAnotherRight());
break;
default:
break;
}
}
public void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.right_layout, fragment);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
}
活动创建时初始化一个右侧碎片,当左侧按钮触发时更换一个右侧碎片
3.3 返回栈
实现了动态添加碎片之后还有一个问题,当点击返回按钮时会直接退出活动,要返回上一个碎片就需要添加一个返回栈
只需要修改replaceFragment方法,调用addToBackStack方法,一般传入null即可
public void replaceFragment(Fragment fragment) {
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction fragmentTransaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
fragmentTransaction.replace(R.id.right_layout, fragment);
fragmentTransaction.addToBackStack(null);
fragmentTransaction.commit();
}
3.4 碎片通信

3.5 碎片生命周期

3.6 使用限定符响应式布局
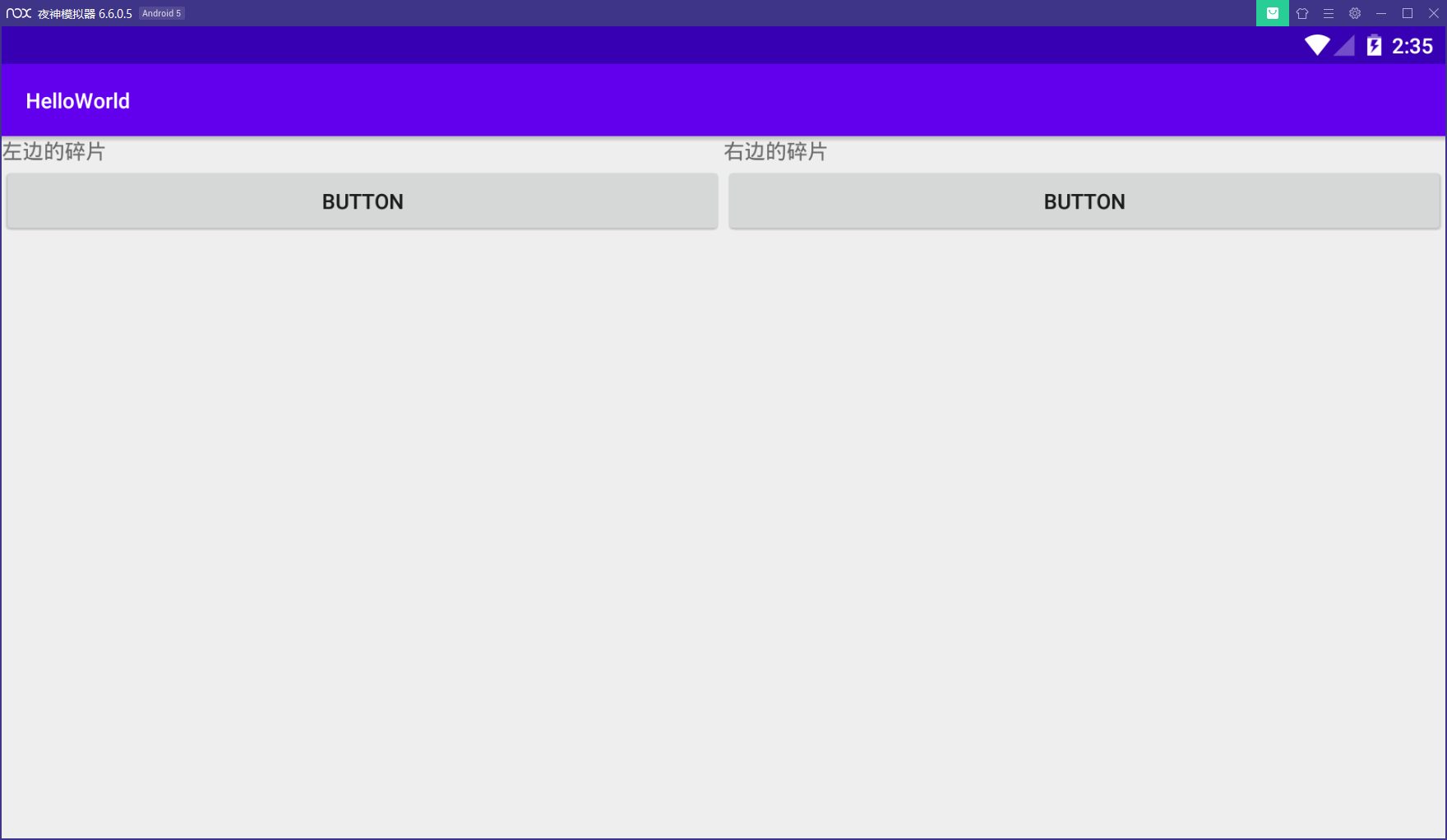
在res目录下新建layout-large或者layout-sw600dp文件夹,新建一个同名的活动布局,当满足条件时,安卓会自动加载相应的布局
普通的布局只有一个fragment大屏设备的引入两个fragment
手机模拟器

平板模拟器
4. 广播机制
4.1 简介
- 标准广播:异步执行,所有的广播接收器会在同一时间接收到广播消息,不能被截断
- 有序广播:同步执行,只有一个接收器能接受广播消息,接收完才能依次执行,可以被截断
4.2 接收广播
4.2.1 动态注册
广播接收器可以动态的对自己感兴趣的广播进行注册,可以在代码中注册也可以在AndroidMainfest中注册,前者称为动态注册,后者称为静态注册
4.2.1.1 动态注册监听网络变化
在代码中进行注册
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private IntentFilter intentFilter;
private NetworkChangeReceiver changeReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
ActivityController.addActivity(this);
// 广播
intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("android.net.conn.CONNECTIVITY_CHANGE");
changeReceiver = new NetworkChangeReceiver();
registerReceiver(changeReceiver, intentFilter);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
unregisterReceiver(changeReceiver);
}
}
public class NetworkChangeReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
ConnectivityManager connectivityManager = (ConnectivityManager)context.getSystemService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);
NetworkInfo networkInfo = connectivityManager.getActiveNetworkInfo();
if(networkInfo != null && networkInfo.isConnected()) {
Toast.makeText(context, "网络已连接", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}else {
Toast.makeText(context, "网络未连接", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
}
connectivityManager.getActiveNetworkInfo();需要添加权限,Android Studio可以自动添加
当网络连接发生变化时会弹出Toast进行消息提示
4.2.2 静态注册
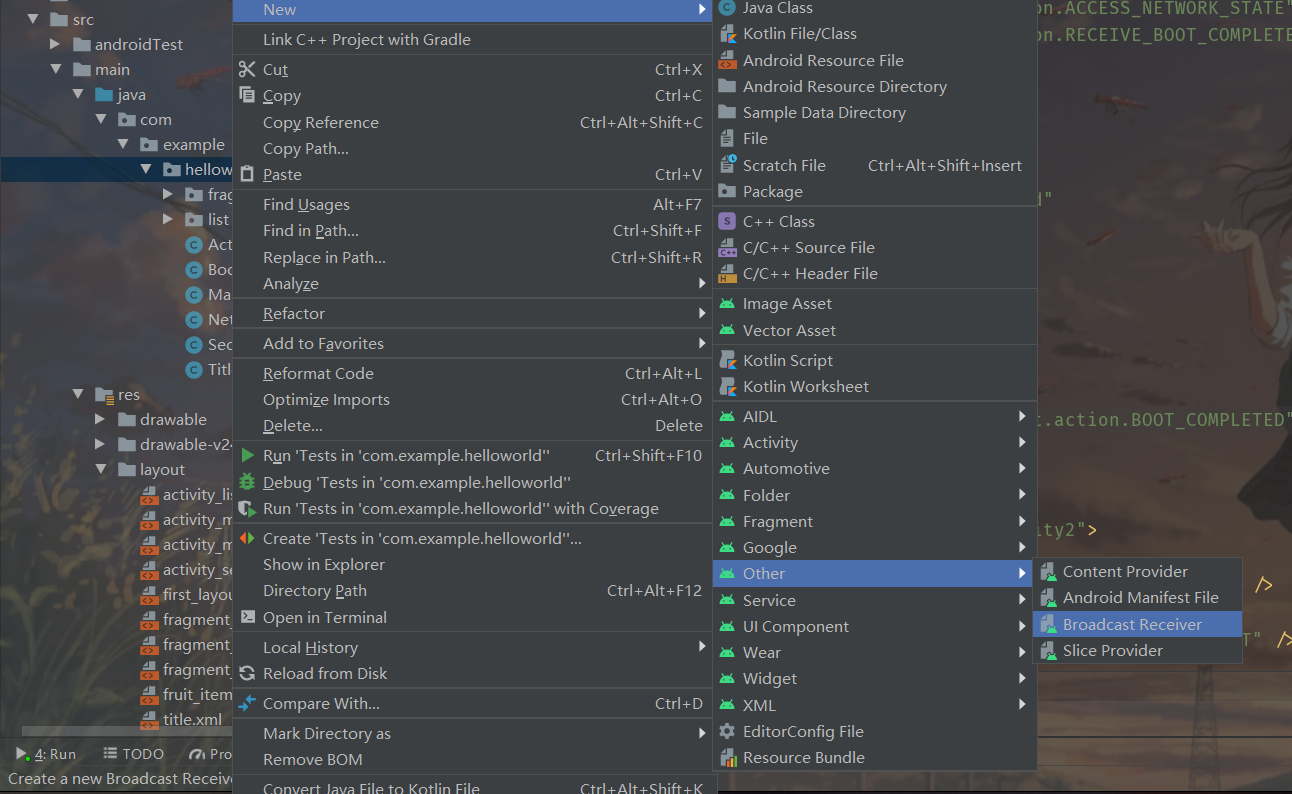
开机自启
new -> other -> Broadcast Recriver
在AndroidMainfest.xml中添加代码
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED" />
···
<application>
···
<receiver
android:name=".BootCompleteReceiver"
android:enabled="true"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.BOOT_COMPLETED"/>
</intent-filter>
</receiver>
</application>
4.3 发送自定义广播
4.3.1 标准广播
新建一个广播接收器,并静态注册,这里的action是自定义的不再是系统服务
在活动中通过按钮发送广播并携带数据
Button btn_receiver = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_receiver);
btn_receiver.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.helloworld.MY_RECEIVER");
intent.putExtra("my_blog", "test");
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
});
在接收器中接收数据并显示
public class MyReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String msg = intent.getStringExtra("my_blog");
Toast.makeText(context, msg, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
4.3.2 有序广播
4.4 本地广播
全局系统的广播存在安全隐患容易被其他程序截获,本地广播只能在程序内部进行传递,提高安全性
导入第三方依赖LocalBroadcastManager
新建本地广播接收器
在活动中动态注册接收器,并添加事件发送广播
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private IntentFilter intentFilter; private LocalBroadcastManager localBroadcastManager; private LocalReceiver localReceiver; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); ActivityController.addActivity(this); intentFilter = new IntentFilter(); localBroadcastManager = LocalBroadcastManager.getInstance(this); intentFilter.addAction("com.example.helloworld.LOCAL_BROADCAST"); localReceiver = new LocalReceiver(); localBroadcastManager.registerReceiver(localReceiver, intentFilter); Button btn_local = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_local); btn_local.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { Intent intent = new Intent("com.example.helloworld.LOCAL_BROADCAST"); intent.putExtra("my_blog", "test local"); localBroadcastManager.sendBroadcast(intent); } }); } @Override public void onDestroy() { super.onDestroy(); localBroadcastManager.unregisterReceiver(localReceiver); } }
本地广播只能动态注册
4.5 最佳实践——强制下线
- 创建广播接收器接收强制下线广播
- 接收器添加提示框提示强制下线
- 关闭所有活动,通过ActivityController
- 重启登陆活动
5. 数据持久化
5.1 文件存储
新建一个文件操作活动,在布局文件中添加一个EditText
<EditText
android:id="@+id/file_edit"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:hint="edit in here" />
5.1.1 将数据存储到文件
在活动中添加代码,编写保存文件的方法并且在活动销毁时触发保存事件
public class FileActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText editText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_file);
editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.file_edit);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
String input = editText.getText().toString();
save(input);
}
public void save(String inputText) {
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = null;
try {
fileOutputStream = openFileOutput("data", Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(fileOutputStream));
bufferedWriter.write(inputText);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(bufferedWriter != null) {
try {
bufferedWriter.close();
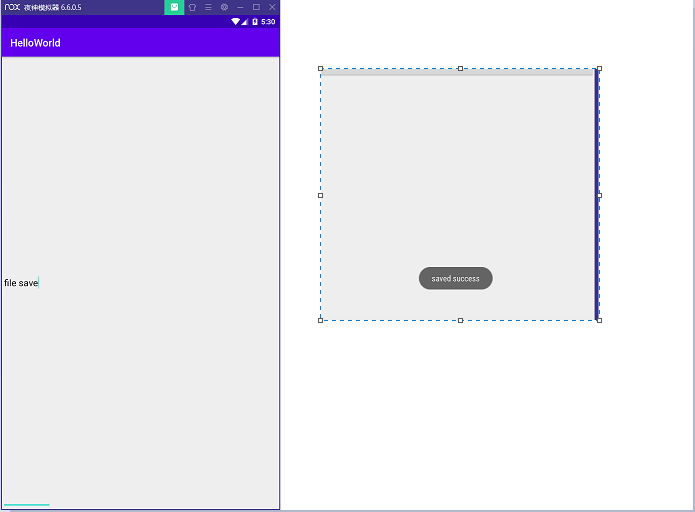
Toast.makeText(FileActivity.this, "saved success", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
5.1.2 从文件中读取数据
在活动中增加加载方法,活动创建时先读取文件,有文件直接加载
public class FileActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private EditText editText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_file);
editText = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.file_edit);
String text = load();
if(!TextUtils.isEmpty(text)) {
editText.setText(text);
editText.setSelection(text.length());
Toast.makeText(FileActivity.this, "loading success", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
···
public String load() {
FileInputStream in = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
try {
in = openFileInput("data");
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line = "";
while((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
content.append(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return content.toString();
}
}

5.2 SharedPreferences存储
存储文件是xml格式
首先创建一个活动,布局中添加两个按钮,一个save一个load
5.2.1将数据存储到SharedPreferences中
首先需要获取SharedPreferences对象,Android中提供了三种方式获取SharedPreferences对象
- Context类中的getSharedPreferences()方法,两个参数:指定SharedPreferences文件名;指定操作模式,目前
只有MODE_PRIVATE可选 - Activity类中getPreferences()方法:只有一个参数:操作模式。(默认当前活动名为SharedPreferences文件名)
- PreferenceManager类中getDefaultSharedPreferences()方法:
静态方法,接收一个Context参数,使用当前包名为前缀来命名SharedPreferences文件
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getSharedPreferences("data_preference", MODE_PRIVATE).edit();
editor.putString("name", "Tom");
editor.putInt("age", 20);
editor.putBoolean("married", false);
editor.apply();
5.2.2从SharedPreferences中读取数据
从上面可以看出SharedPreferences存储文件非常简单,读取文件更为简便,从SharedPreferences对象中一系列get方法即可获得数据
SharedPreferences editor_load = getSharedPreferences("data_preference", MODE_PRIVATE);
String name = editor_load.getString("name", "");
int age = editor_load.getInt("age", 0);
Boolean married = editor_load.getBoolean("married", false);
5.2.3 代码及效果展示
public class PreferencesActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_preferences);
Button btn_save = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_preference_save);
btn_save.setOnClickListener(this);
Button btn_load = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_preference_load);
btn_load.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn_preference_save:
SharedPreferences.Editor editor = getSharedPreferences("data_preference", MODE_PRIVATE).edit();
editor.putString("name", "Tom");
editor.putInt("age", 20);
editor.putBoolean("married", false);
editor.apply();
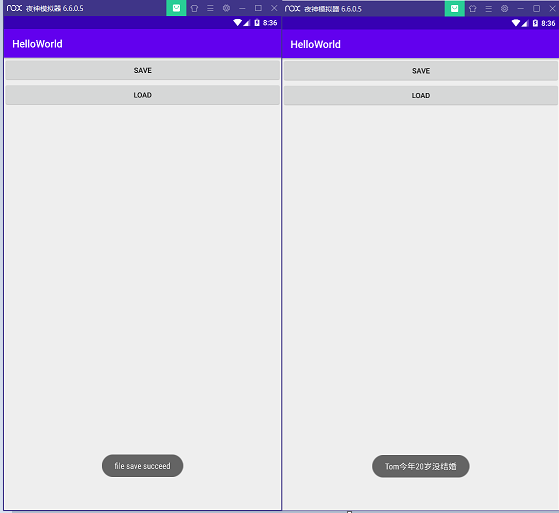
Toast.makeText(PreferencesActivity.this, "file save succeed", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
case R.id.btn_preference_load:
SharedPreferences editor_load = getSharedPreferences("data_preference", MODE_PRIVATE);
String name = editor_load.getString("name", "");
int age = editor_load.getInt("age", 0);
Boolean married = editor_load.getBoolean("married", false);
String marry = married?"结婚了":"没结婚";
Toast.makeText(PreferencesActivity.this, name+"今年"+age+"岁"+marry, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
5.3 数据库SQLite
SQLite是一款轻量级关系数据库,支持SQL语法,遵循ACID
5.3.1 创建数据库
略
5.3.2 LitePal操作数据库
通过JavaBean操作数据库
引入依赖
LitePal
配置xml映射
app.src.main目录下新建assets目录,新建litepal.xml配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?>
<litepal>
<dbname value="BookStore" />
<version value="1" />
<list></list>
</litepal>
修改Mainfest,application新加属性android:name="org.litepal.LitePalApplication"
创建数据库
创建JavaBean
添加活动代码,当数据库访问一次之后就创建了

对数据进行操作需要让JavaBean继承DataSupport
添加数据

更新数据
一种方法是将要修改的数据值全部set然后save在set要修改的值再次save
另一种方法用updateAll
book.setPrice(14.5);
book.updateAll("name = ? and author = ?", "Tom","第一行代码");
设置要修改的价格,然后使用updateAll方法,方法中的参数是约束条件,当当与where查询,只修改匹配到的信息
删除数据
使用DataSupport中的deleteAll方法,第一个参数是眼删除的表名,第二个参数是查询条件
DataSupport.deleteAll(Book.class, "price < ?", "14");
查询数据
使用 List<Book> list = DataSupport.findAll(Book.class);可以将所有的数据返回到一个List中

此外,还支持原生查询
Cursor cursor = DataSupport.findBySQL("select * from book where name = ?", "第一行代码");
返回的是一个Cuesor对象,需要将数据一一取出
6. 跨程序共享数据——内容提供器
6.1 运行时权限
安卓6.0以上加入了运行时权限,危险权限需要用户授权
参考代码
public class PermissionActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
List<String> contacts = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_permission);
ListView list = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list_contact);
adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, contacts);
list.setAdapter(adapter);
if (ContextCompat.checkSelfPermission(PermissionActivity.this, Manifest.permission.READ_CONTACTS)
!= PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(PermissionActivity.this, new String[]{Manifest.permission.READ_CONTACTS}, 1);
} else {
readContacts();
}
}
private void readContacts() {
Cursor cursor = null;
try {
cursor = getContentResolver().query(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.CONTENT_URI, null, null, null, null);
if(cursor != null) {
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
String name = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.DISPLAY_NAME));
String number = cursor.getString(cursor.getColumnIndex(ContactsContract.CommonDataKinds.Phone.NUMBER));
contacts.add(name+ "\n" +number);
}
adapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(cursor != null) {
cursor.close();
}
}
}
@Override
public void onRequestPermissionsResult(int requestCode, @NonNull String[] permissions, @NonNull int[] grantResults) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults);
switch (requestCode) {
case 1:
if (grantResults.length > 0 && grantResults[0] == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
readContacts();
} else {
Toast.makeText(PermissionActivity.this, "no permission", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
6.2 创建内容提供器
7. 运用手机多媒体
7.1 使用通知
首先获取通知管理器对象,然后创建通知对象,通过通知管理器下发通知,每个通知的id都是不同的
代码示例通过按钮触发通知
Button btn_notification = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_notification);
btn_notification.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification notification = new Notification.Builder(PermissionActivity.this)
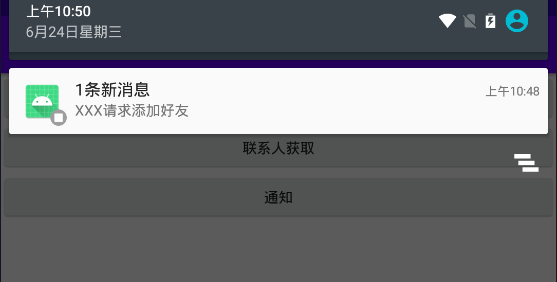
.setContentTitle("1条新消息")
.setContentText("XXX请求添加好友")
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.build();
manager.notify(1, notification);
}
});
这里可以看到按钮点击之后通知栏显示了一条通知
但是,这里的通知不能点击,要再让它可以点击
这时需要用到PendingIntent,可以理解为延时的Intent
将代码稍作改装,就得到了可以点击的通知
Button btn_notification = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_notification);
btn_notification.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent(PermissionActivity.this, MainActivity.class);
PendingIntent pendingIntent = PendingIntent.getActivity(PermissionActivity.this, 0, intent, 0);
NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE);
Notification notification = new Notification.Builder(PermissionActivity.this)
.setContentTitle("1条新消息")
.setContentText("XXX请求添加好友")
.setWhen(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setSmallIcon(R.mipmap.ic_launcher)
.setLargeIcon(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.ic_launcher))
.setContentIntent(pendingIntent)
.build();
manager.notify(1, notification);
}
});
距离完成还差一步,点击通知之后通知应该是消失的
有两种方法:
通知追加setAutoCancel方法
··· .setAutoCancel(true)通过通知管理器的canael方法根据通知id消除通知
··· NotificationManager manager = (NotificationManager)getSystemService(NOTIFICATION_SERVICE); manager.cancel(1)
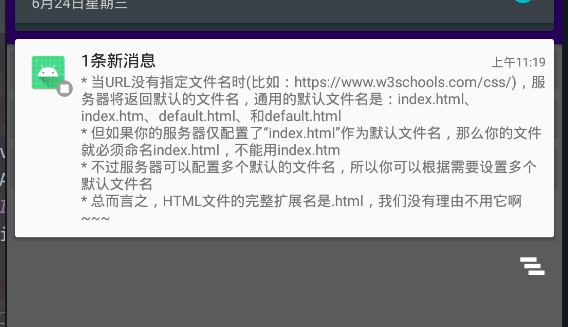
长文本通知
.setStyle(new Notification.BigTextStyle().bigText("* 当URL没有指定文件名时(比如:https://www.w3schools.com/css/)," +
"服务器将返回默认的文件名," +
"通用的默认文件名是:index.html、index.htm、default.html、和default.html\n" +
"* 但如果你的服务器仅配置了“index.html”作为默认文件名,那么你的文件就必须命名index.html,不能用index.htm\n" +
"* 不过服务器可以配置多个默认的文件名,所以你可以根据需要设置多个默认文件名\n" +
"* 总而言之,HTML文件的完整扩展名是.html,我们没有理由不用它啊~~~"))
图片通知:
.setStyle(new Notification.BigPictureStyle().bigPicture(BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.drawable.wj)))
7.2 调用摄像头和相册
8. 网络
8.1 webView
应用程序内引入网页,不需要打开系统浏览器
创建活动,布局添加webview组件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".WebActivity">
<WebView
android:id="@+id/web_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
编辑活动代码
public class WebActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@SuppressLint("SetJavaScriptEnabled")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_web);
WebView webView = (WebView)findViewById(R.id.web_view);
// 设置允许js,否则网页逻辑可能无法运行
webView.getSettings().setJavaScriptEnabled(true);
webView.setWebViewClient(new WebViewClient());
webView.loadUrl("http://www.baidu.com");
}
}
该活动需要网络权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
8.2 HTTP协议访问网络
8.2.1 HttpURLConnection
安卓上发送HTTP请求有两种方式HttpURLConnection和HttpClient,由于HttpClientd的API数量多,扩展困难已经在6.0被移除
创建布局
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn_http"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="HTTP请求" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_http"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
编辑活动代码
public class WebActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
TextView responseText;
@SuppressLint("SetJavaScriptEnabled")
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_web);
Button sentRequest = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn_http);
responseText = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.text_http);
sentRequest.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
sendRequestWithHttpURLConnection();
}
});
}
private void sendRequestWithHttpURLConnection() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 创建HttpURLConnection对象
HttpURLConnection connection = null;
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
// URL
URL url = new URL("http://www.baidu.com");
connection = (HttpURLConnection)url.openConnection();// 建立连接
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");// 请求方式
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000);// 超时时间
connection.setReadTimeout(8000);
InputStream in = connection.getInputStream(); // 获取输入流
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(line);
}
showResponse(response.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 完成后需要关闭连接
if(reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(connection != null) {
connection.disconnect();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
private void showResponse(final String response) {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
responseText.setText(response);
}
});
}
}
耗时的操作不能再主线程中进行,开一个线程处理;
new Thread().start;不要忽略start更新UI不能在子线程中,会闪退,通过runOnUiThread切换回主线程
POST请求
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");// 请求方式
DataOutputStream out = new DataOutputStream(connection.getOutputStream());
out.writeBytes("name=Tom&password=123456");
在获取输入流之前把要提交的数据写入
8.2.2 使用OKHttp
在AndroidX中添加依赖okhttp(squareup公司的)
添加新的方法使用OkHttp,把button的绑定事件改为sendRequestWithOkHttp
private void sendRequestWithOkHttp() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://www.baidu.com").build();
Response response = client.newCall(request).execute();
String responseData = Objects.requireNonNull(response.body()).string();
showResponse(responseData);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
就可以看到跟原来一样的效果
8.3 解析XML数据
进行网络传输通常有两种格式XML和JSON
课本P334
8.4 解析JSON数据

使用GSON
添加依赖gson
可以把JSON的格式映射成一个对象


8.5 网络方法封装
将网络方法封装到HttpUtil类中,方法作为静态方法直接调用
如
public class HttpUtil {
public static void sendGetRequestWithOkHttp(String address, okhttp3.Callback callback) {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(address)
.build();
client.newCall(request).enqueue(callback);
}
}
调用
private void sendRequestWithOkHttp() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
HttpUtil.sendGetRequestWithOkHttp("http://www.baidu.com", new okhttp3.Callback() {
@Override
public void onResponse(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull Response response) throws IOException {
String responseData = Objects.requireNonNull(response.body()).string();
showResponse(responseData);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(@NotNull Call call, @NotNull IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}).start();
}