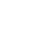上次使用 Vuex4.0 的时候带来的体验不能说很差吧,可以说是非常不好,类型支持需要自定义等等问题让我将目光转向了社区中的新兴势力——Pinia
Pinia 是一个用于 Vue 的状态管理库,类似 Vuex, 是 Vue 的另一种状态管理方案
Pinia 支持 Vue2 和 Vue3
Pinia 对比 Vuex 的优势:
- Pinia 的 API 设计非常接近
Vuex 5的提案。(作者是 Vue 核心团队成员) - 无需像
Vuex 4自定义复杂的类型来支持 typescript,天生具备完美的类型推断。 - 模块化设计,你引入的每一个 store 在打包时都可以自动拆分他们。
- 无嵌套结构,但你可以在任意的 store 之间交叉组合使用。
- Pinia 与 Vue devtools 挂钩,不会影响 Vue 3 开发体验。
pinia 的使用架构如下
从 Vuex 转 Pinia 简直不要太简单,下面来看一下 Pinia 的 Guide
store
pinia 中创建并挂载 pinia 的过程只有一步
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import App from './App.vue'
createApp(App)
.use(createPinia())
.mount('#app')
然后就可以开始定义 store 了,定义 store 的时候跟 Vuex 的 module 有些类似,但是不需要那么繁琐,定义不同的 store 模块然后直接在代码中引入使用即可。
定义一个 store 的方式如下
export default defineStore('count', {
state: () => ({}),
actions: {},
getters: {}
})
使用 store 时直接引入对应的 store 即可
<template>
<div>{{ store.count }}</div>
<div>{{ store.doubleCount }}</div>
<button @click="store.increment">+</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import useCountStore from '../store/counter'
const store = useCountStore()
</script>

在组件之外的其他地方使用 store
// 不要在函数之外使用 store
const store = useStore()
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// we wanted to use the store here
if (store.isLoggedIn) next()
else next('/login')
})
// 在回调内部使用 store, 能保证 store 运行在它应该运行的地方
router.beforeEach((to) => {
const store = useStore()
if (to.meta.requiresAuth && !store.isLoggedIn) return '/login'
})
state
state 用来存储数据状态,需要传入一个函数,并且将所有的 state 作为 object 返回。
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
const useStore = defineStore('storeId', {
state: () => {
return {
counter: 0,
name: 'Eduardo',
isAdmin: true,
}
},
// 可以直接使用 state: () => ({})
})
// 直接使用 store 实例来范文 state
const store = useStore()
store.counter // 0
store.$reset() // 重置store状态
更新 state
与 Vuex3.0不同的是,pinia 允许直接修改 state 的值,同时也提供了 patch 方法来同时更新多个 state
store.$patch({
counter: store.counter + 1,
name: 'Abalam',
})
但是,使用此语法应用某些更改确实很困难或成本很高:任何集合修改(例如,从数组中推送、删除、拼接元素)都需要您创建一个新集合。正因为如此,该$patch方法还接受一个函数来对这种难以应用补丁对象的突变进行分组:
store.$patch((state) => {
state.items.push({ name: 'shoes', quantity: 1 })
state.hasChanged = true
})
覆盖 state
可以通过将商店的$state属性设置为新对象来替换商店的整个状态
store.$state = { counter: 666, name: 'Paimon' }
订阅状态
可以通过$subscribe()一个 store的方法来观察 state 和它的变化,类似于 Vuex 的subscribe 方法。使用$subscribe()常规的优点watch()是订阅只会在补丁后触发一次(例如,当使用上面的功能版本时)。
<template>
<div>{{ store.count }}</div>
<div>{{ store.name }}</div>
<button @click="store.$patch({ count: 10, name: 'king' })">change</button>
</template>
<script setup lang="ts">
import useCountStore from '../store/counter'
const store = useCountStore()
store.$subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log('store changed', state, mutation)
})
</script>
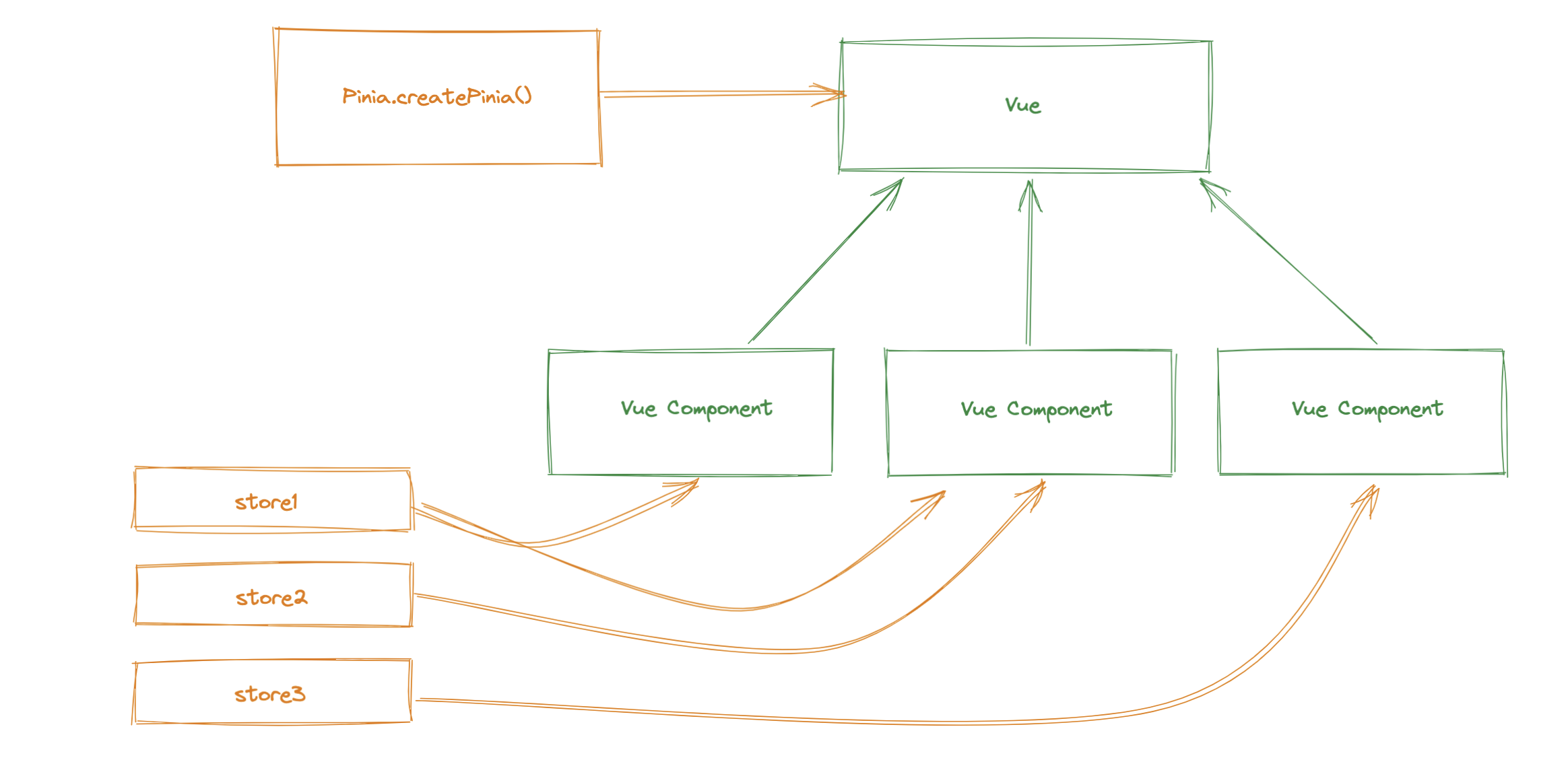
每次 store 更新之后都会触发传入的回调,我们这里使用 dispath 来跟新多个 state 看一下效果
默认情况下组件内的订阅将在组件卸载之后一同卸载,如果想将订阅保留可以传如第二个参数
const someStore = useSomeStore()
someStore.$subscribe(callback, true)
getters
getters用于组合 state(计算值)
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export default defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({ count: 0 }),
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2 // also use this.count
}
}
})
getters也可以接收参数
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export default defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({ count: 0 }),
actions: {
increment() {
this.count += 1
}
},
getters: {
doubleCount(state) {
return state.count * 2
},
customMultiple(state) {
return (multiple: number) => state.count * multiple
}
}
})
getters 可以使用其他 store 的 getters 作为条件计算
import useUserStore from './user'
getters: {
doubleCount(state): string {
const userStore = useUserStore()
return `${state.count * 2}---${userStore.name}`
},
customMultiple(state) {
return (multiple: number) => state.count * multiple
}
}
getters 会自动推导返回的类型,但是由于可以使用其他store 的 getters,所以尽量手动标注这写 getters 的返回值类型
actions
actions 用于处理逻辑,他可以是异步的,在 action 函数内部使用 this 可以获取到 state 中的数据
export default defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({ count: 0 }),
actions: {
increment() {
this.count += 1
throw new Error('error')
}
}
})
同样的,actions 中也可以使用其他的 store 中的数据
actions 中也可以添加 state 中订阅的类似操作,当actions 触发时使用回调处理
const countStore = useCountStore()
countStore.$onAction(({ name, store, args, after, onError }) => {
after((result) => console.log('after', result))
onError((error) => console.error('onError', error))
console.log('store action')
console.log(name, store, args)
})
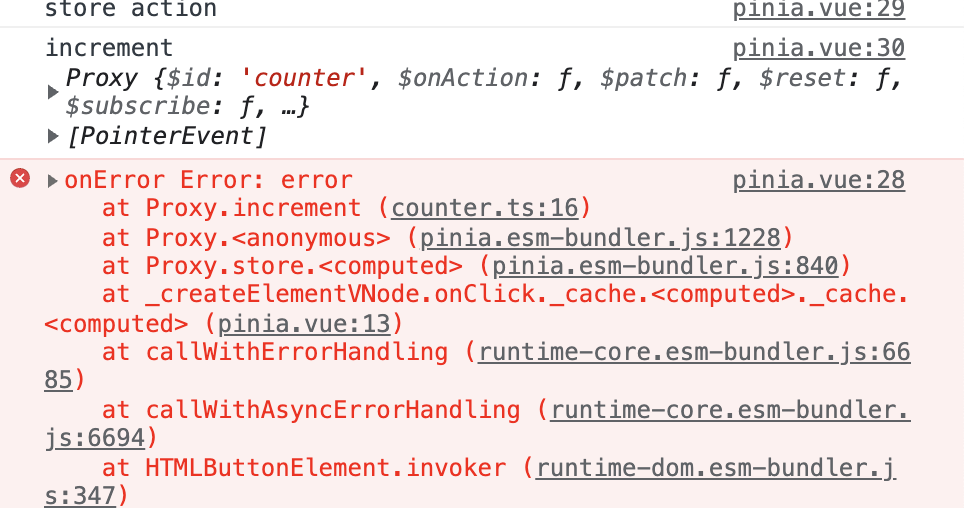
after钩子会在 action 执行完之后执行,当 action 抛出异常时会执行 onError 钩子
onAction 也会跟随组件销毁,同样可以让其在组件销毁时保留下来
someStore.$onAction(callback, true)